【GASE】EditCell Virology Platform, broad-spectrum antivirals, SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19
Author: Yu- An Kung / Shin-Ru Shih
The research and development team from Chang Gung University (CGU)/Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH) in collaboration with National Health Research Institutes (NHRI), and Rutgers University Medical School has been devoting tremendous efforts on antiviral research to fight COVID-19.
Research Center for Emerging Viral Infections (RCEVI, the Featured Areas Research Program supported by Ministry of Education and Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan) at CGU and Clinical Virology Laboratory at CGMH have successfully isolated 32 strains of SARS-CoV-2 virus under the biosafety guideline from Taiwan CDC. These strains serve as precious materials for antiviral assays to develop drugs against COVID-19. Moreover, the team applied EditCell Virology platform (genome-wide CRISPR-based system) to screen host factors that are important for RNA virus replication. They identified X protein as a crucial factor not only for coronaviruses but also for flaviviruses and enteroviruses infections. Based on this finding, the team also identified two FDA-approved drugs targeting to X protein, that are able to decrease the viral load of these RNA viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, the only cause of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The team is now seeking the opportunity with international pharmaceutical companies to conduct clinical trials, which may treat COVID-19 patients and contain virus spread.
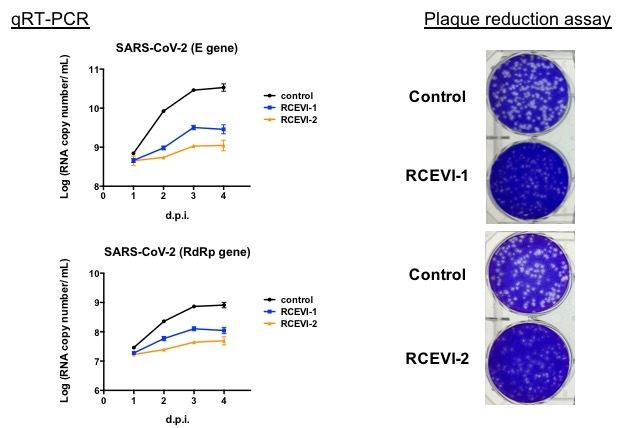
Figure 1. Antiviral effects of RCEVI-1 and RCEVI-2 on SARS-CoV-2 by quantitative real-time PCR and plaque reduction assay.
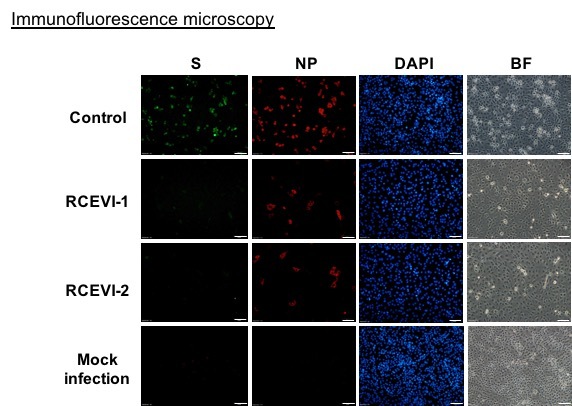
Figure 2. RCEVI-1 and RCEVI-2 show inhibitory effects on SARS- CoV-2 infection by immunofluorescence microscopy

